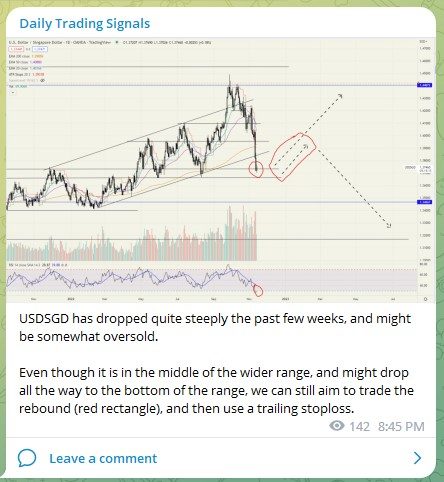
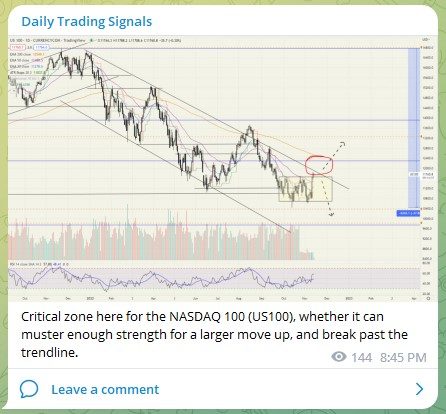
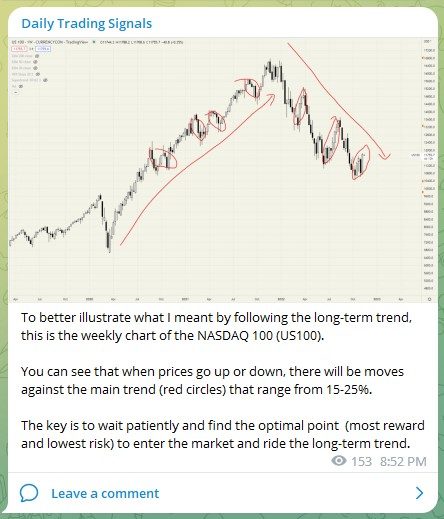
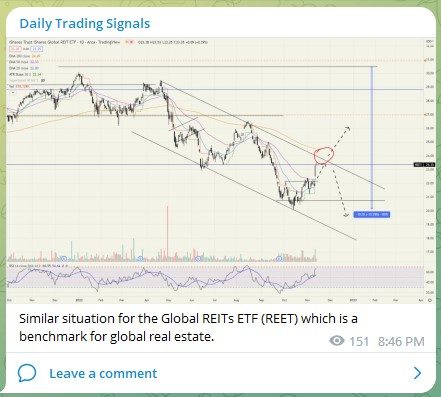
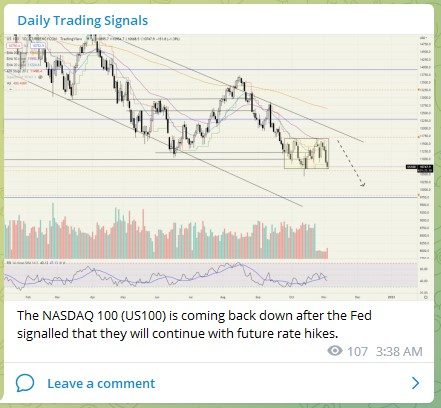
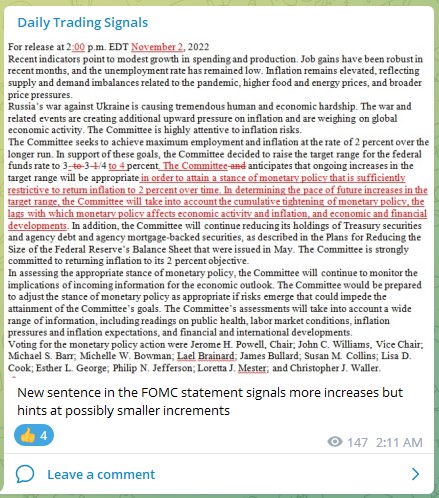
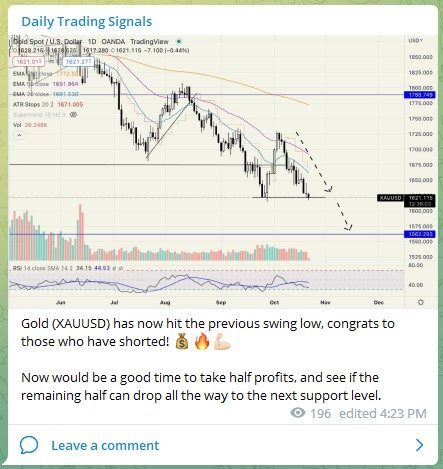
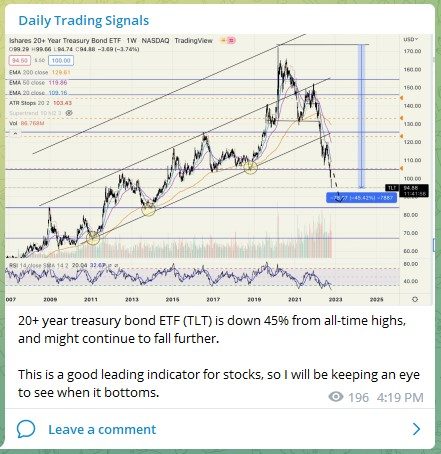
Entering the world of cryptocurrencies is like stepping into a new dimension, with products such as stablecoins, NFTs, DeFi, Bitcoin, and many more coming out every single day.
It’s hard to keep up with everything, even for the most experienced traders. That’s why it’s important to know what you’re doing and where you’re headed before jumping in.
One of the most interesting but underrated products on the market today is stablecoins.
For those who don’t know, a stablecoin is a cryptocurrency that is pegged to an asset with a stable value.
The most popular and well-known stablecoin is Tether (USDT).
In this blog post, I’m going to cover the basics of stablecoins, before going in depth on what Tether (USDT) is, how it works, and whether or not it is a good investment.

What is a Stablecoin?
A stablecoin is simply a digital asset that is pegged to a stable asset, such as the U.S. dollar.
The main advantage of a stablecoin is that it allows traders to avoid the volatility of the crypto markets while still enjoying the benefits of blockchain technology.
Also, with stablecoins, you can be sure that the value of your money will not fluctuate.
Why are Stablecoins Useful?
Stability is one of the essential features of any currency.
If a currency’s value fluctuates too much, it is impossible to use it in everyday life.
Stablecoins are pegged to an asset that is highly stable and unlikely to experience rapid changes in price over short periods.
Their stability makes them useful as a holding currency for saving, investment and transactions.
Now that you are armed with the right information about stablecoins, let’s move on to Tether (USDT).
What is Tether (USDT)?
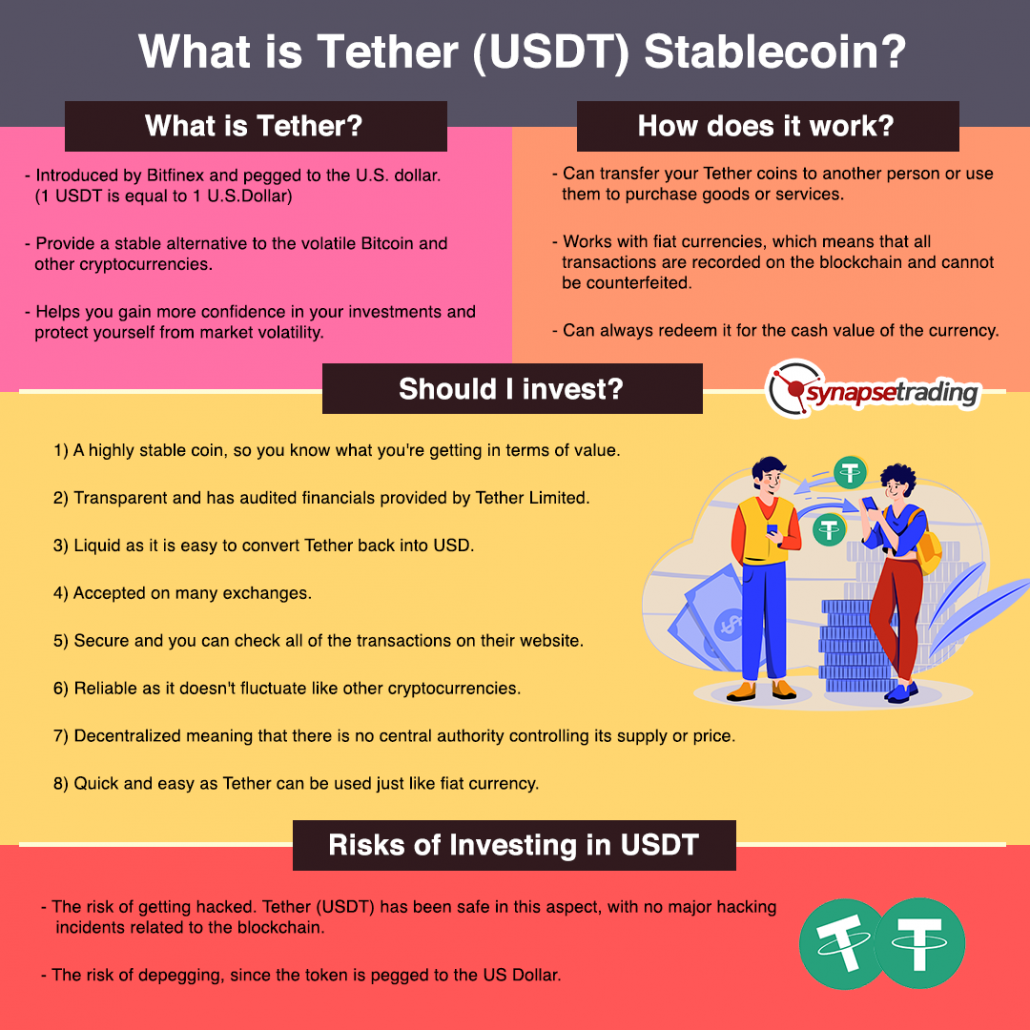
Tether is a digital currency introduced by Bitfinex, a cryptocurrency exchange platform.
It is a tether-based stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar.
In simple words, one USDT is equal to one U.S. Dollar.
This means that if you have one Tether coin, then its value will remain the same, and you can use it as a substitute for USD currency.
The main function of Tether is to provide a stable alternative to traditional cryptocurrencies, which tend to be more volatile.
This helps protect you from market volatility, so if you are worried about the security of your funds, then you can use Tether as a safe haven to hold your funds.
How Does Tether (USDT) Work?
Tether (USDT) works in the same way as other cryptocurrencies do.
You can transfer your Tether coins to another person or use them to purchase goods or services.
You can also store your USDT in a digital wallet, which is similar to a bank account.
As with other cryptocurrencies, all transactions for USDT are recorded on the blockchain and cannot be counterfeited.
Furthermore, the company behind Tether guarantees that every USDT is backed by a U.S. dollar held in reserve.
This means you can always redeem it for the cash value of the currency.
If you want to convert your USDT back into fiat, all you need to do is contact customer support and request a refund.
Reasons for Investing in Tether (USDT)
As we all know, Tether is one of the most popular stablecoins on the market.
It offers investors a secure alternative to volatile cryptocurrency investments while also providing opportunities for arbitrage and hedging.
Here are some of the smart key reasons why you should invest in Tether:
1. High Stability
Tether is a highly stable coin, so you know what you’re getting in terms of value.
It doesn’t fluctuate much and can be used for a variety of purposes, including as an investment, a store of value, or simply as a means to pay for goods and services online.
This makes it a go-about choice for those who want to protect their wealth from market volatility while still having access to the benefits of blockchain technology.
2. Transparent
Tether is very transparent in its accounts and reserves, and it has audited financials provided by Tether Limited.
No doubt Tether is one of the most transparent cryptocurrencies on the market today.
The company provides an audit report that details how much USDT there is in circulation and where it came from, which means you can rest assured your money isn’t being used for anything unethical.
3. Liquidity
The next most important thing to look for when choosing a stablecoin is liquidity.
When you want to convert USD into Tether, and Tether back into USD, it should be easy and quick.
You don’t want to have to wait days or weeks for your money!
Tether has maintained high levels of liquidity since its inception in 2014, which means you can be confident that you’ll be able to cash out of USDT whenever you need it.
4. Accepted on Many Exchanges
Many exchanges accept Tether, so it’s easy to trade with other cryptocurrencies.
Tether is the most widely accepted stablecoin in the world.
Many exchanges accept Tether as a way to deposit funds, so if you want to buy other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, you can deposit USDT into your brokerage account, then use that to buy other cryptocurrencies.
5. Security
Tether is 100% transparent, which means that you can see all of the transactions on their website.
This is paramount because it makes it easy for people to know how much money there is in circulation and how many tethers are being held by each exchange.
6. Reliable
Tether is a reliable cryptocurrency because it’s one of the most stable in the market.
It doesn’t fluctuate like other cryptocurrencies, which makes it great for people who want to make long-term investments or get stable yields via yield-farming, but also want to preserve the capital.
7. Decentralized
Tether is decentralized, which means that there is no central authority controlling its supply or price.
This makes it easier for anyone to use cryptocurrency without having to worry about regulations or restrictions from governments.
8. Quick and Easy
Tether is very easy to use because it can be used just like fiat currency.
Anyone who wants to buy Tether will only need a wallet and an internet connection; this makes it more convenient than other cryptocurrencies that require complicated mining procedures.
Risks of Investing in Tether (USDT)
Just with any stablecoin, there are risk associated with investing in USDT.
One of the main risk for cryptocurrencies is always the risk of getting hacked, but so far Tether (USDT) has been safe in this aspect, with no major hacking incidents related to the blockchain.
The other major risk for stablecoins is the risk of depegging, since the token is pegged to the US Dollar.
If depegging occurs, like what happened to Terra USD (UST), then the token can rapidly spiral to zero.
However, Tether has a healthy reserve to defend the peg, and the price has not deviated significantly from the peg before, so this risk is not too high as well.
How to Buy Tether (USDT)?
To buy Tether, you will need to register an account on an exchange that supports USDT, such as Bitfinex, Binance, or Huobi.
Once you have your exchange account set up and verified, you will be able to purchase Tether with either fiat currency or another cryptocurrency.
For more information about brokerages, you can check out our list of tools & resources.
The Future of Tether (USDT)
Tether, or USDT for short, is issued on the Omni Layer, a blockchain platform that is compatible with multiple cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum.
Each USDT unit you go for is backed by one U.S. dollar held in reserve by Tether Limited.
And with its recent expansion into Ethereum and other blockchain platforms, Tether’s future looks bright.
Concluding Thoughts
Tether is currently the go-to option for many people looking to use stablecoins, as it’s an ideal way to store your hard-earned money without having to worry about it losing value.
Furthermore, the fact that it’s backed by USD makes it a more stable option than other cryptocurrencies.
However, if you are looking for higher yields on stablecoins, then there are other stablecoins which offer higher yields, but also come with higher risk.
So in a sense, Tether (USDT) is like the blue-chip of stablecoins in the crypto universe.
Now that you know all about stablecoins and Tether (USDT), do you think they are good investments?
What do you think are some good strategies to profit from stablecoins such as USDT?
Let me know in the comments below.