The 3Ms of Trading are Methodology, Money Management, and Mindset, and they each play a crucial role in your success in trading.
As a trader, you will need to master all 3 Ms, but you also need to know the relative importance of each factor.
In this post, I will explain how each factor affects your trading success, and which factors you should be focusing on to improve your trading.
What to Focus on in Trading?
Having studied many professional traders, I found that there are 3 crucial factors that have led to their success.
All these market wizards have found success because they have understood and mastered the 3Ms of trading – Method, Money and Mindset.
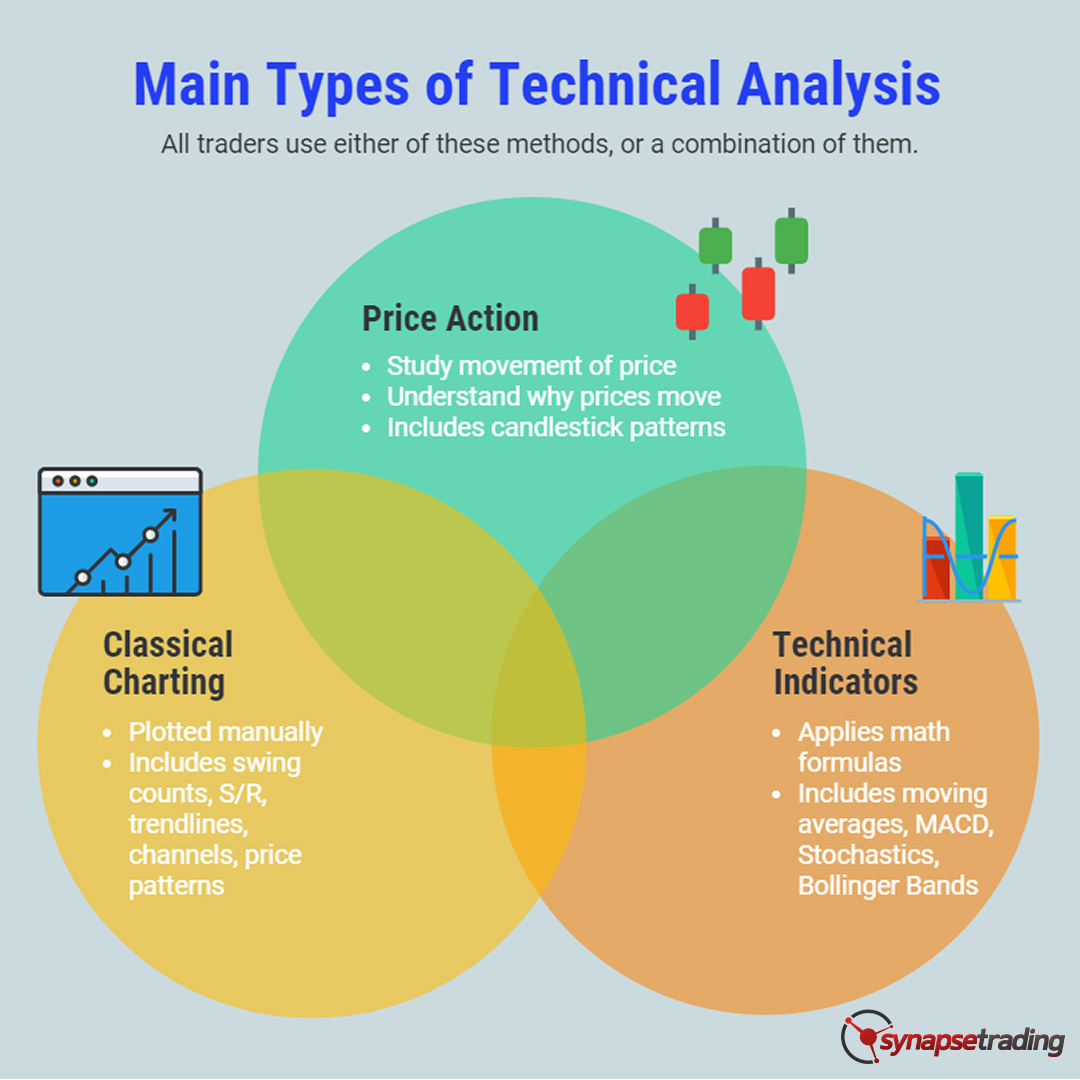
Method (methodology): Process by which a trader enters into the market, using either technical or fundamental inputs to make their decision
Money (risk management): This includes capital allocation, risk parameters (drawdown limits), risk-to-reward calculations (entry price, profit target, stoploss)
Mindset (psychology): Market psychology the most important part of trading, and determines how well you can execute your trading plan in the markets in real time
To many new traders who know of these 3Ms, they tend to make the mistake of giving equal weightage to all 3 parts (refer to above), or even worse, almost 100% weightage to the “Method”.
The psychology (mindset) is the hardest part of trading because emotions like greed and fear run wild once your money is at stake in the market.
Hence, your degree of rational analysis is only limited to how well you can manage your psychology.
Without the execution, the plan is useless. The money and risk management is also essential because it ensures your survival and consistency in the markets.
After all, the number one rule is capital preservation.
“Don’t focus on making money; focus on protecting what you have.” – Paul Tudor Jones
Methodology (10% Focus)
Methodology refers to your method of analysis, your strategy, your setups, basically the basis on which you make your buying and selling decisions.
As we will be covering in greater detail in other blog posts, I will not be elaborating too much on this here.
For now, all you need to know is that the most common tools used to make such decisions are technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or some combination of both.
Money Management (30% Focus)
Money management, or risk management, refers to how well you use your trading capital, to maximize your returns, while at the same time minimizing your risk.
This includes your capital allocation per trade, such as the 2% money management rule, and also things like risk paramaters for each trade, such as maximum drawdown limits.
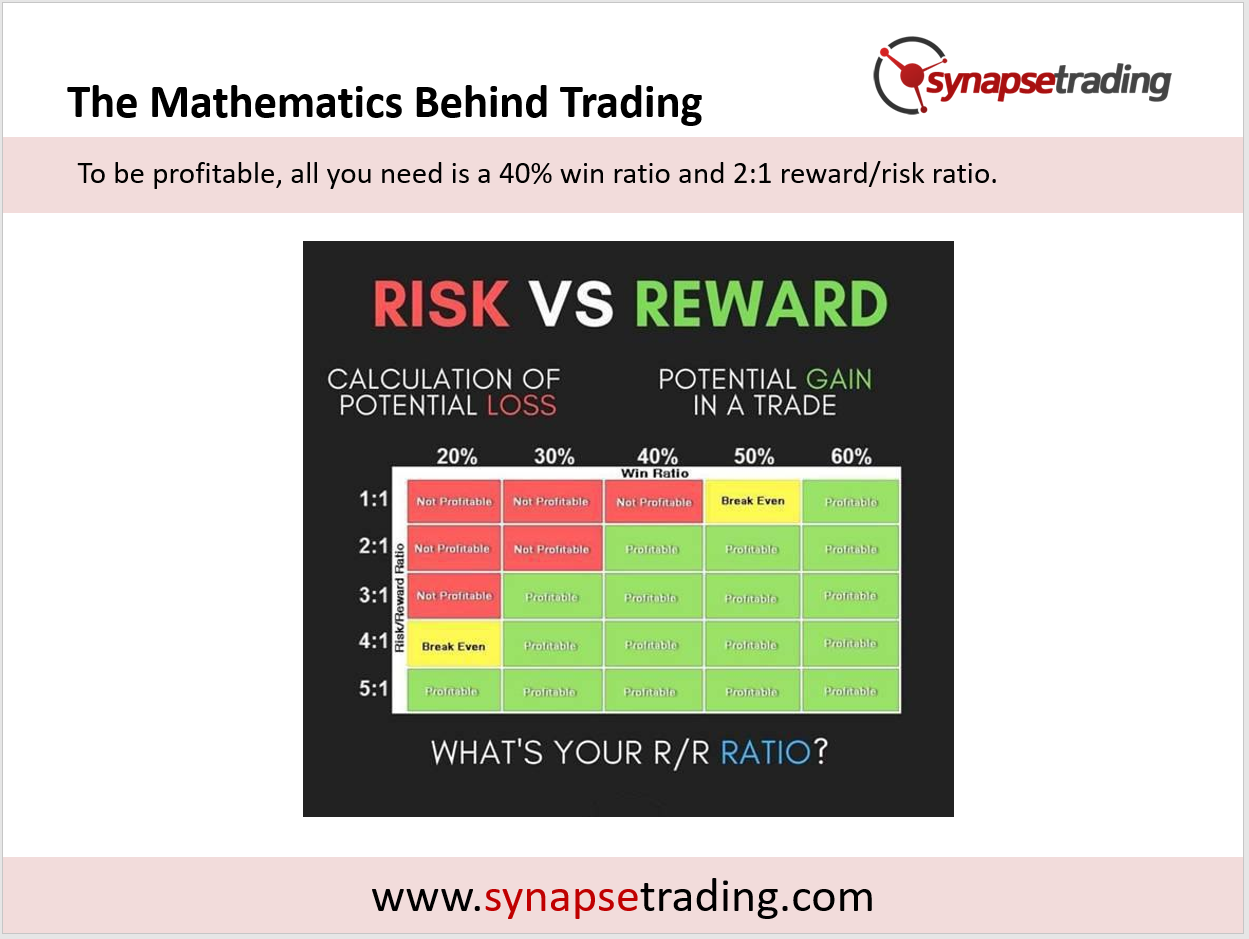
This means that for each trade, you will need to decide on the entry price (EP), stoploss price (SL), and target profit (TP) before you make each trade, so that you will be able to calculate the reward-to-risk (RR) ratio to decide whether it is worth taking the trade.
To be profitable in trading, all you need is a good balance between the win ratio (aka. hitrate) and the reward to risk ratio, to ensure that you have a net positive expectation on every trade.
For example, if you have a 40% win ratio, and your reward/risk ratio is 2, you will still end up net profitable in the long run.
Mindset (60% Focus)
The mindset, or trading psychology, is definitely the most important aspect of trading, and it is also the hardest to master.
This will determine how well you can make good decisions under stress, and consistently execute your trading plan without getting swayed by emotions.
Thinking accurately requires a certain level of self-awareness, so that we can avoid any behavioral biases that skew our rational thinking and decision-making process.
Summary
In conclusion, to be successful in trading, you need to master all the 3Ms, but the problem for most traders is they only tend to focus on 1 or 2 factors, and neglect the rest.
As a result, they might become very good at analysing charts (methodology), but remain poor at money management and trading psychology.
To improve your trading, the faster way to do so is to work on whatever you are weakest at, because that has the most room for improvement.
Now that I have shared the 3 important elements of trading, which do you think you are lacking the most, and will have the biggest impact on your trading if you work on improving it?
Let me know in the comments below.

If you would like to learn how to get started in trading, also check out: “The Beginner’s Guide to Trading & Technical Analysis”
After trading for 18 years, reading 1500+ books, and mentoring 1000+ traders, I specialise in helping people improve their trading results, by using tested trading strategies, and making better decisions via decision science.