How Place Trades (Buy & Sell) on Interactive Brokers (IBKR)
Weekly AMA on Instagram - Ask me anything about trading & investing, stock picks, market analysis, etc!
Before reading this guide, the first thing you will need to do is to open an Interactive Brokers (IBKR) account, before you can start trading.
Table of Contents
How Place Trades (Buy & Sell Orders)
1. Click on “Trade”.
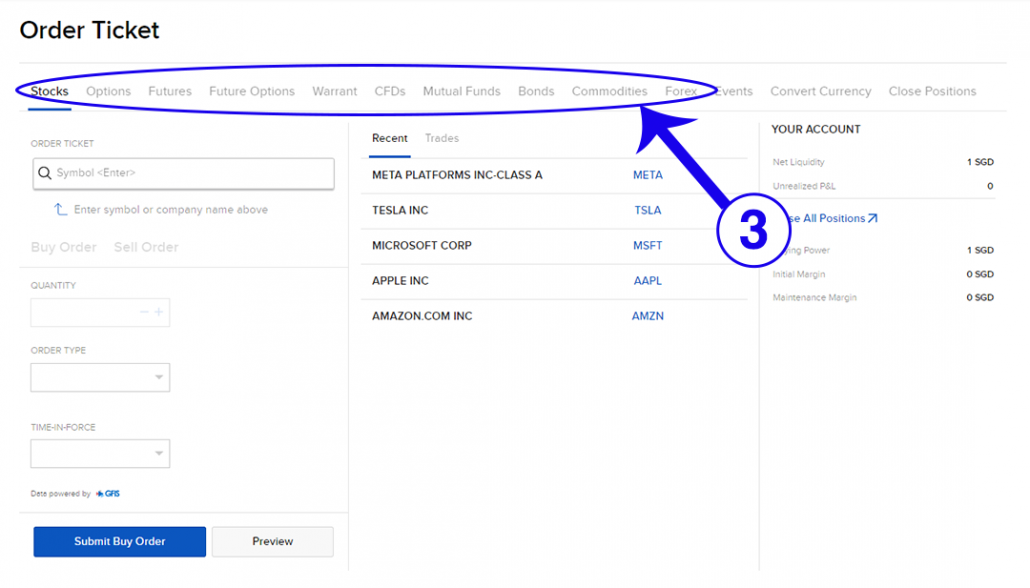
2. Click on “Order Ticket”.

3. Choose which products that you will like to trade.
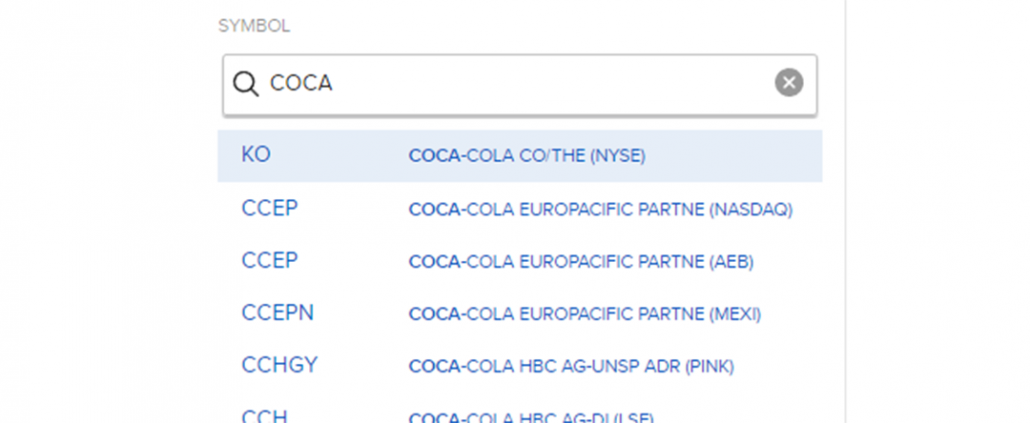
4. For example, I will like to purchase 2 stocks of Coca-Cola. I will key in the company name and press enter.

5. Select the correct product you are looking for.
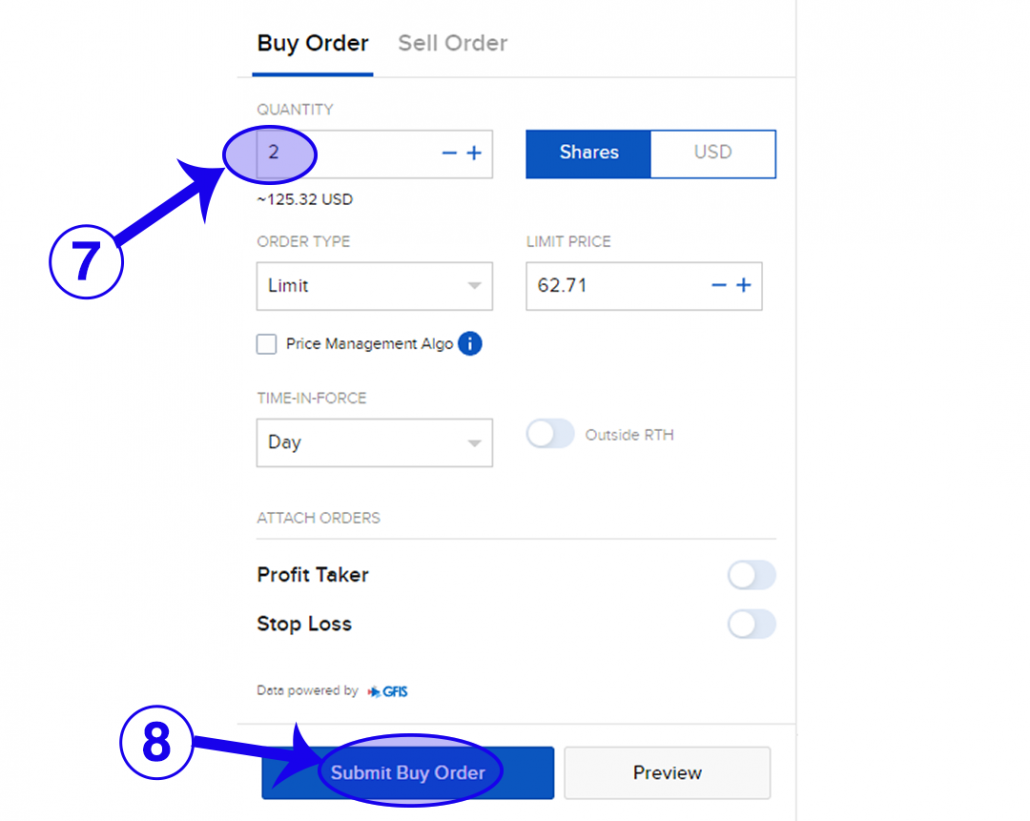
6. The page will update accordingly. Click on “Buy”.
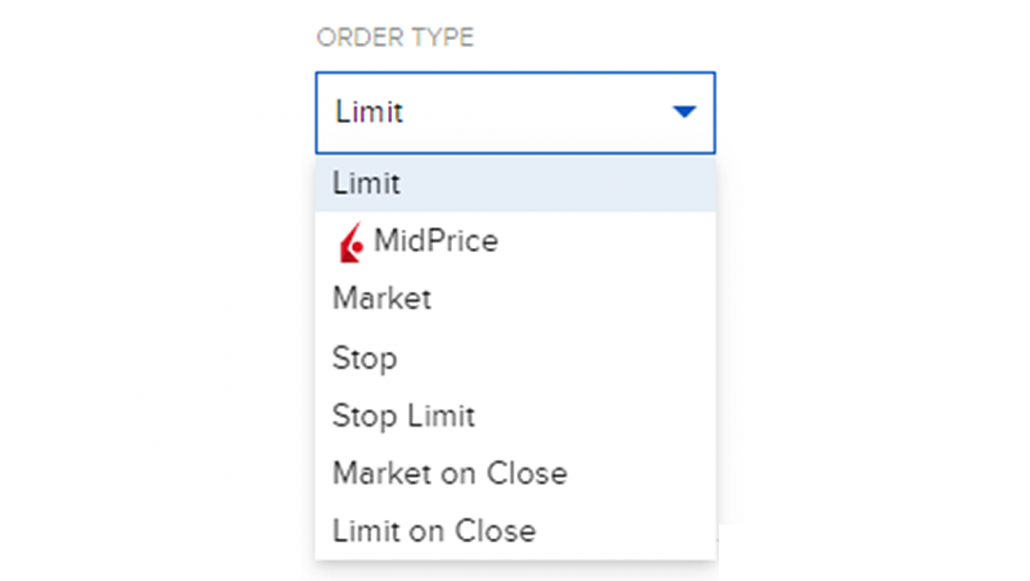
7. Adjust the quantity to 2. (For more information on Order Type, Time-in-force and Attach Orders, check after step 8)
8. Click on “Submit Order” to purchase the 2 stocks! That’s it!
Types of Trade Orders
Limit: A Limit order is an order to buy or sell at a specified price or better. The Limit order ensures that if the order fills, it will not fill at a price less favorable than your limit price, but it does not guarantee a fill.
MidPrice: The MidPrice order is designed to split the difference between the bid and ask prices, and fill at the current midpoint of the NBBO (National Best Bid and Offer) or better. Set an optional price cap to define the highest price (for a buy order) or the lowest price (for a sell order) you are willing to accept.
Market: A Market order is an order to buy or sell at the market bid or offer price. A market order may increase the likelihood of a fill and the speed of execution, but unlike the Limit order a Market order provides no price protection and may fill at a price far lower/higher than the current displayed bid/ask.
Stop: A Stop order is an instruction to submit a buy or sell market order if and when the user-specified stop trigger price is attained or penetrated. A Stop order is not guaranteed a specific execution price and may execute significantly away from its stop price. A Sell Stop order is always placed below the current market price and is typically used to limit a loss or protect a profit on a long stock position. A Buy Stop order is always placed above the current market price. It is typically used to limit a loss or help protect a profit on a short sale.
Stop Limit: A Stop-Limit order is an instruction to submit a buy or sell limit order when the user-specified stop trigger price is attained or penetrated. The order has two basic components: the stop price and the limit price. When a trade has occurred at or through the stop price, the order becomes executable and enters the market as a limit order, which is an order to buy or sell at a specified price or better.
A Stop-Limit eliminates the price risk associated with a stop order where the execution price cannot be guaranteed, but exposes the investor to the risk that the order may never fill even if the stop price is reached. The investor could “miss the market” altogether.
Market on Close: A Market-on-Close (MOC) order is a market order that is submitted to execute as close to the closing price as possible.
Limit on Close: A Limit-on-close (LOC) order will be submitted at the close and will execute if the closing price is at or better than the submitted limit price.
Time-in-Force for Orders
The time in force for an order defines the length of time over which an order will continue working before it is cancelled.
Good Till Cancel: An order that uses the Good-Til-Canceled (GTC) time in force will continue to work until the order fills or is cancelled . The ability to enter a bid well below the prevailing trading price for most asset classes, or an offer higher than its current level, allows an investor to place a resting order for days, weeks or months in advance without having to repeat the process each day.
At the Opening: Use this to send a market-on-open (MOO) or limit-on-open (LOO) order.
Day: A Day order is canceled if it does not execute by the close of the trading day. Unless otherwise specified, every order is a Day order.
Attach Orders

Profit Taker: It is an opposite side limit order designed to close a position while it is profitable. (For example, you purchase a stock at $10 each. You can indicate your PT LIMIT PRICE at $11 to make a profit of $1 per stock)
Stop Loss: It is an opposite side stop order designed to close out a position with only a user-specified, limited loss. (For example, you purchase a stock at $10 each. You can indicate your SL STOP PRICE at $9 to cut your losses if the stock is plummeting)
If you found this guide useful, you might also want to check out our full list of guides for Interactive Brokers!
 New to Trading? Make your first live trade today in this workshop! Meet Spencer live for 3 hours of hands-on training! No prior experience required! Learn all the basics of trading, and step-by-step guidance to make your first trade!
New to Trading? Make your first live trade today in this workshop! Meet Spencer live for 3 hours of hands-on training! No prior experience required! Learn all the basics of trading, and step-by-step guidance to make your first trade!
 If you're looking for the best trading opportunities every day across various markets, and don't want to spend hours doing the research yourself, check out our private Telegram channel!
If you're looking for the best trading opportunities every day across various markets, and don't want to spend hours doing the research yourself, check out our private Telegram channel!
Spencer is an avid globetrotter who achieved financial freedom in his 20s, while trading & teaching across 70+ countries. As a former professional trader in private equity and proprietary funds, he has over 15 years of market experience, and has been featured on more than 20 occasions in the media.









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!