How to Stake on Proof-of-Stake Blockchains for Passive Crypto Income
Join our Telegram channel for more market analysis & trading tips: t.me/synapsetrading
Did you know that you can generate additional passive income just by staking your existing crypto holdings?
Proof of stake (PoS) is an alternative to proof of work (PoW) that is being increasingly used in crypto blockchains, where nodes are rewarded for validating transactions instead of miners working to earn coins through their processing power.
The good news is that the process tends to be much easier than mining and also generates passive income on the side.
So, how do you stake your crypto?
In this blog post, I will explain what this new proof of stake system is all about, and how you can stake your crypto on this system to generate passive income.
Table of Contents
Understanding DeFi
DeFi, or decentralized finance, is a growing ecosystem of financial protocols and applications built on the Ethereum blockchain.
DeFi represents the shift from traditional, centralized financial systems to peer-to-peer finance enabled by decentralized technologies built on the Ethereum blockchain.
DeFi protocols offer a wide range of services, from lending and borrowing platforms to stablecoins and tokenized BTC.
Using DeFi protocols, you can earn interest on your crypto, trade with leverage, and do much more. And with over $63 billion worth of value locked in Ethereum smart contracts, it is clear that DeFi is here to stay.
With this increased ease of access to investment opportunities, there are more and more DeFi projects being created every day.
Some notable examples include MakerDAO Dai stablecoin, Augur prediction market platform, and Compound (COMP) leveraged cryptocurrency interest accounts.
Basic PoS Terminology
Before we dive any deeper, let’s go over some basic PoS terminology:
- A stake is simply the amount of cryptocurrency you have staked.
- The stakeholder is the person who stakes their cryptocurrency.
- A validator is a node that creates new blocks on the blockchain.
- The block reward is the amount of cryptocurrency rewarded to the validator for creating a new block.
- Delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS) is a type of PoS where stakeholders can delegate their staking power to a validator.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
To understand how proof of stake works, we must first understand what a consensus algorithm is.
A consensus algorithm is a set of rules that everyone in a network agrees upon to validate transactions and prevent fraud.
The most popular consensus algorithm is called proof of work, which is used by Bitcoin.
However, there are many other consensus algorithms that have been developed, including proof of stake.
Proof of stake is a popular type of consensus algorithm, by which a cryptocurrency blockchain network aims to achieve distributed consensus.
The term “proof of stake” was coined by a “Bitcointalk forum” user called QuantumMechanic.
The fundamental point was that it would be wasteful to open up mining to everyone and let them compete against one another.
Therefore, in PoS-based cryptocurrencies, the creator of the next block is chosen via various combinations of random selection and wealth or age (i.e., the stake).
Unlike proof of work-based systems, there is no concept of blocks being mined — rather, validators are staking their own crypto holdings to have their blocks included in the chain.
Bear in mind that the validators are not chosen in a completely arbitrary fashion.
A certain amount of coins must be staked into the network by a node before it can be considered for the validator’s role.
The size of the stake has a bearing on the probability that a validator will be chosen to forge the next block.
Let’s assume that John contributes $100 to the network while Cindy contributes $500.
Cindy’s chances of making the cut to forge the next block are five times higher!
It is worth noting that the stake is always more than what the validator earns from the transaction fees to keep the validator financially motivated.
Among the many blockchain networks, such as Polkadot (DOT), Algorand (ALGO), Solana (SOL), Cardano (ADA), and the upcoming Ethereum 2.0, proof of stake represents an evolution in consensus algorithms.
How To Stake Tokens in a PoS Network?
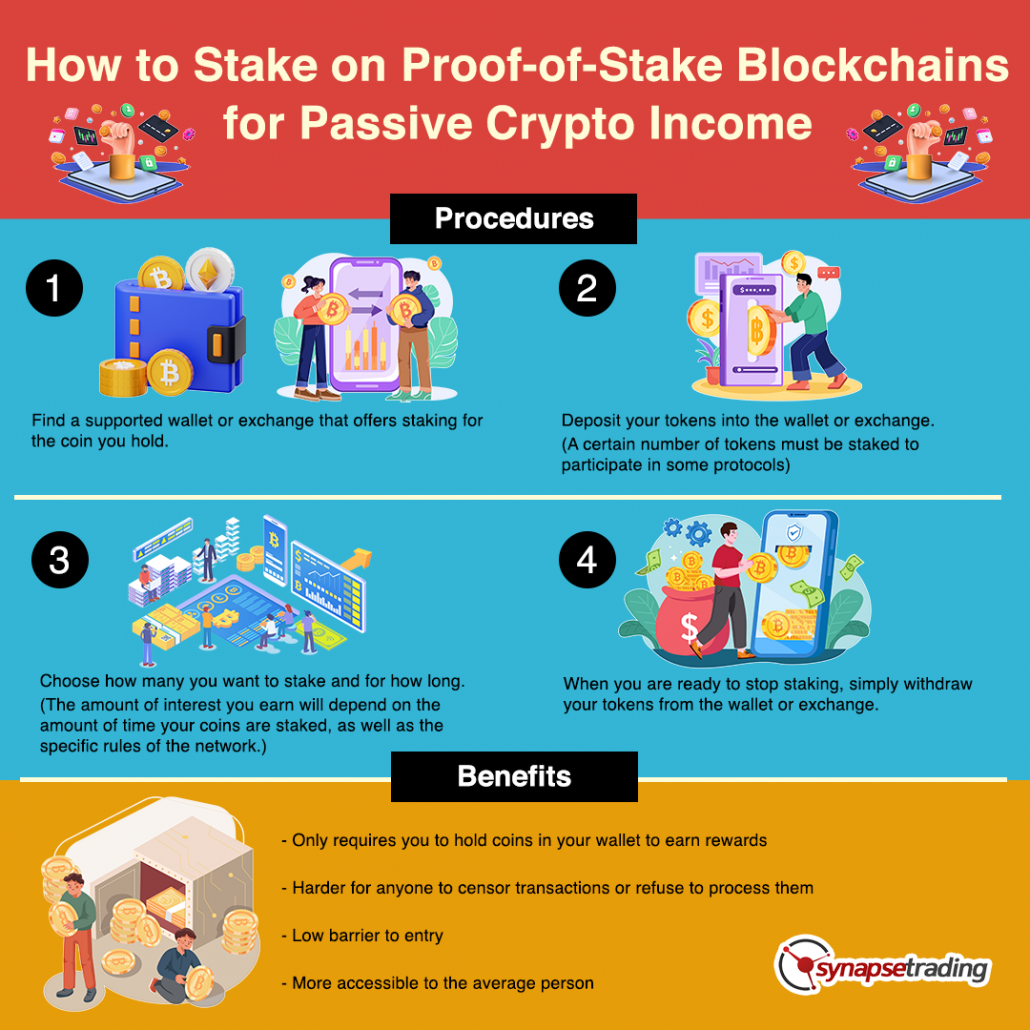
To stake tokens in a PoS network, you first need to find a supported wallet or exchange that offers staking for the coin you hold.
Then, you will need to deposit your tokens into the wallet or exchange.
Keep in mind that a certain number of tokens must be staked to participate in some protocols.
For example, to stake on Tezos, you will need a minimum of 8,000 Tezos (XTZ).
The PoS implementation in Ethereum 2.0 will call for 32 ether (ETH).
Once your tokens are deposited, you can choose how many you want to stake and for how long.
The amount of interest you earn will depend on the amount of time your coins are staked, as well as the specific rules of the network.
For example, some networks may require that you keep your coins staked for a minimum of 30 days, while others have no minimum requirement.
In any case, the longer you stake your tokens, the more rewards you will earn.
The good news is that once you have deposited your coins into a staking wallet, the process is completely passive — meaning you can earn interest without having to do any work.
There are many coins that can give you an Annual Percentage Yield (APY) of 4-8% or even higher, so the income potential in staking is relatively high.
When you are ready to stop staking, simply withdraw your tokens from the wallet or exchange.
Why Should You Stake for Passive Income?
Proof of stake blockchains offer a unique opportunity for earning passive income from cryptocurrency.
Unlike proof of work blockchains, which require mining equipment and expensive electricity, proof of stake blockchains only require you to hold coins in your wallet to earn rewards since you are not solving complex mathematical problems.
This makes staking a much more accessible way to earn crypto.
PoS algorithms also tend to be more censorship resistant than PoW algorithms.
This is because, in a PoS system, the network is not controlled by a small group of miners who can choose to censor certain transactions.
Instead, everyone who has a stake in the network (i.e., everyone who owns coins) has a say in what happens.
This makes it much harder for anyone to censor transactions or refuse to process them.
Issues with Proof of Stake
While PoS does away with mining (and, in theory, reduces energy consumption), it has its own set of issues.
Firstly, no PoS system today can scale to the level of Bitcoin or Ethereum.
These systems are not yet as decentralized or safe as the most advanced PoW systems.
However, these flaws could be fixed with more advanced consensus mechanisms like Casper (CSPR).
When the validator does not show up to complete their job, this might be another source of possible issues.
However, this problem can also be easily solved by choosing a large number of backup validators in case the primary ones fail.
And though PoS systems might use fewer resources overall, they can be less secure than PoW systems.
One reason is that the hashing power in a PoS system is spread out among all users, while in a PoW system, it is centralized among miners.
This means that a PoS system is more vulnerable to a Sybil attack, where an attacker creates multiple fake identities to gain control of the network.
Another issue with PoS is that it can be more vulnerable to 51% attacks, where one entity controls more than half of the currency.
The blockchain is also technically at risk of fork if two different blocks are created at exactly the same time and one gets included in a new block before being confirmed by a sufficient number of validators, depending on your staking setup.
To increase security in such cases, many projects use vaults where stakeholder deposits are locked up until they can be periodically released and rewarded with new coins (i.e., interest on your crypto holdings).
One popular alternative is so-called delegative proof of stake, which involves stakers delegating their stake to another party who will stake on their behalf.
Concluding Thoughts
To summarize, in Proof of Stake blockchain networks, the miners do not actually mine the coins.
Instead, they essentially lock up their coins for a set amount of time and take turns validating transactions on the network.
In return, these stakers receive rewards based on the number of coins they have staked and their specific network’s staking fee schedule.
So if you are looking for a way to earn some passive income from your cryptocurrency holdings, staking might be the perfect solution.
Staking is the process of holding onto your coins to support the network and earn rewards.
By doing so, you can earn interest on your holdings and help keep the network secure.
Now that you know how staking works and how it earns you passive income from your crypto holdings, would you consider staking your crypto tokens?
Do you think the reward to risk profile of such an investment is better than those in traditional finance?
Let me know in the comments below.

If you would like to learn more about crypto & DeFi, also check out: “The Ultimate Guide to Blockchain & Cryptocurrencies”
 Our flagship mentoring program is suitable for both beginners and advanced traders, covering the 4 strategies which I used over the past 15 years to build up my 7-figure personal trading portfolio.
Our flagship mentoring program is suitable for both beginners and advanced traders, covering the 4 strategies which I used over the past 15 years to build up my 7-figure personal trading portfolio.
 If you're looking for a reputable brokerage that covers all products (SG stocks, US stocks, global stocks, bonds, ETFs, REITs, forex, futures, crypto) and has one of the lowest commissions, this is what I currently use.
If you're looking for a reputable brokerage that covers all products (SG stocks, US stocks, global stocks, bonds, ETFs, REITs, forex, futures, crypto) and has one of the lowest commissions, this is what I currently use.
After trading for 18 years, reading 1500+ books, and mentoring 1000+ traders, I specialise in helping people improve their trading results, by using tested trading strategies, and making better decisions via decision science.





Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!